It is a cherished desire of parents to raise their children in an emotionally healthy home where each child feels loved and has a deep sense of belonging. Most parents do everything within their control to ensure each child feels safe within the family unit and that there is a harmonious relationship among members of the family. However, not all parents realise this esteemed ideal. Some children grow up with strained sibling relationships that last into adulthood.
This post will address sibling rivalry which is a common sibling problem within families today. Upon reading, you will gain an in-depth understanding of:
- How siblings affect each other as they grow in the same household
- What is sibling rivalry
- Factors that lead to sibling rivalry
- How sibling rivalry manifests itself
- How to manage sibling rivalry

How siblings affect each other
Most children have siblings and half-siblings i.e brothers and sisters with whom they share one or both parents. Children play a significant role in shaping family dynamics as well as contributing to each individual child’s growth and development.
Sibling relationships are some of the long-lasting relations individuals have.
This relationship starts from infancy and last way into adulthood. It is therefore imperative for parents to know the impact of these relationships both to the family and how they affect the children as they grow together into adulthood.
1. Emotional Development
Siblings play a crucial role in shaping each other’s emotional development. They provide companionship, support and empathy. This emotional availability contributes to the development of social skills, emotional intelligence and the ability to navigate other relationships that siblings form e.g friendships and romantic relationships.
2. Socialisation
Siblings serve as important socializing agents for each other. They learn and practice social skills, negotiation, conflict resolution and cooperation within the sibling relationship. Siblings influence each other’s behavior, values and beliefs, shaping their social interactions both within and outside the family.
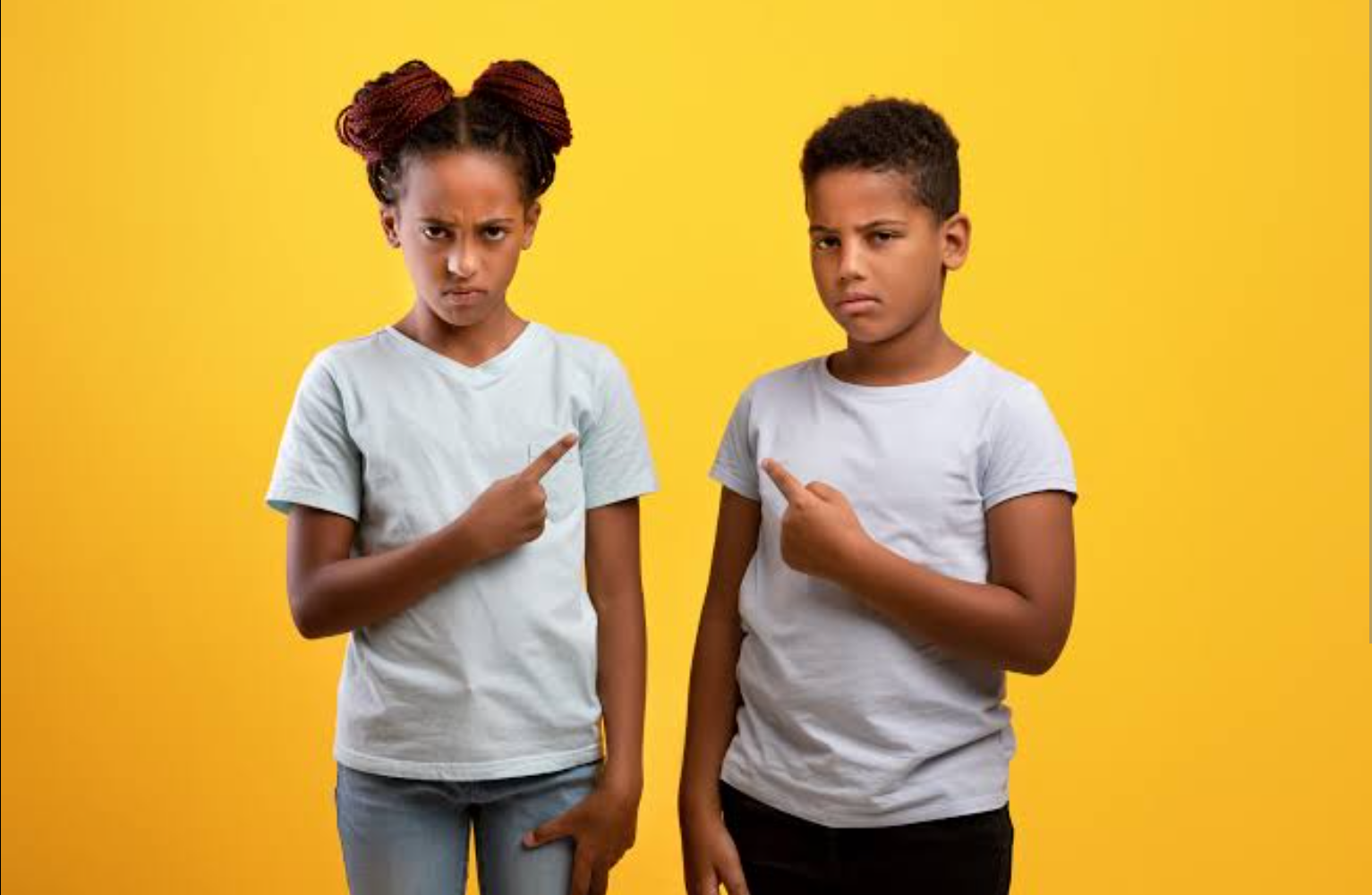
3. Competition and Rivalry
Siblings often experience competition and rivalry, which can have both positive and negative effects. Healthy competition can motivate siblings to excel, achieve goals and develop important skills. However, excessive rivalry and constant comparison can lead to resentment, low self-esteem and strained sibling relationships.
4. Learning and Intellectual Development
Siblings influence each other’s intellectual growth and academic achievement. They engage in joint activities, share knowledge and stimulate each other’s curiosity from early childhood. Siblings also provide academic support, assistance with homework and engage in intellectual discussions, contributing to their cognitive development.
5. Identity Formation
Siblings play a significant role in shaping each other’s identity. They serve as role models, provide immediate feedback and influence each other’s sense of self. To a large extent, siblings do influence choices related to interests, hobbies and values, contributing to the development of individual children within the family.
6. Social Support and Lifelong Bonds
Siblings often develop strong emotional bonds and provide lifelong support to each other. They can be a source of comfort, advice and companionship throughout different life stages of growth and development including adulthood. If well nurtured, sibling relationships can offer a lifelong sense of belonging and provide a reliable support system during challenging times.

What Is Sibling Rivalry?
Sibling rivalry comprises of the emotional and behavioral conflicts that occur between siblings.
It is rooted in feelings of sibling comparisons, envy or perceived favouritism. It involves a complex mix of love for each other, competition and a desire for individuality. These factors shape the dynamics and interactions within the sibling relationship, each intensifying sibling’s competition for attention, resources and parental affection. Sibling rivalry can range from mild to severe and not all siblings will exhibit sibling rivalry.
Factors That Lead To Sibling Rivalry
Sibling rivalry can have various causes and multiple factors can contribute to its occurrence. Here are some common causes of sibling rivalry:
1. Age Differences and Developmental Stages
Siblings who are close in age or at similar developmental stages may experience more rivalry as they compete for parental and friend’s attention, resources and the rate at which they hit developmental milestones. Age-related differences in abilities and privileges can create a sense of inequality and fuel rivalry.
2. Competition for Parental Attention
Siblings often compete for their parents’ time, affection and approval. The arrival of a new sibling or changes in family dynamics, such as parental divorce or remarriage can intensify the competition for attention, affection and attachment which might trigger feelings of jealousy and resentment within siblings.
3. Differences in Temperament and Personalities
Siblings with contrasting personalities and temperaments may clash more frequently, leading to rivalry. Differences in traits such as introversion versus extroversion, competitiveness versus cooperativeness or compliance versus rebellion can create conflicts and misunderstandings within sibling relationships.
4. Perceived Favouritism
The perception of favoritism by parents can contribute significantly to sibling rivalry. When a child feels that a sibling is receiving more attention, praise or privileges from parents, it can lead to feelings of resentment towards a sibling. This arises due to a sense of unfair treatment from the parent fueling the rivalry between siblings.
5. Limited Resources and Space
Siblings may engage in rivalry when resources, such as toys, bedrooms or parental time are perceived as scarce or limited. The need to share or divide resources can lead to conflicts and competition for fairness, ownership or control.
6. Sibling Comparison
Comparisons made by parents, extended family or society can intensify sibling rivalry. When siblings are constantly compared to each other in terms of achievements, abilities, beauty, intelligence or behavior, it can create a hostile environment and breed rivalry.
7. Parental Influence and Modeling
Parental behaviors, attitudes, and interactions with their children can impact sibling relationships. If parents model and encourage competitive or combative behavior, it can contribute to the development of rivalry among siblings. Also, if parents engage in triangulation which refers to a communication pattern where the parent avoids direct interaction with one child, instead using another child as an intermediary. This can create misunderstandings and conflicts between siblings. Often triangulation serves as a manipulative strategy to control or gain power over children.
8. Family Dynamics
The overall family dynamics and atmosphere can influence sibling relationships and contribute to rivalry. Factors such as parental stress, marital conflict or parental favoritism can exacerbate sibling rivalry within the family.
It’s important to note that sibling rivalry can vary greatly in intensity and frequency among different families and individuals. Understanding the underlying causes can help parents and caregivers address and manage sibling rivalry effectively, promoting healthier relationships between siblings.
How Sibling Rivalry Manifests Itself
Sibling rivalry manifests itself in different ways. These manifestations vary depending on individual personalities of children. Further, these manifestations change as the children undergo different growth and developmental stages. As a parent, you can align your parenting to mitigate adverse effects of sibling rivalry as soon as you see any of the following manifestations:
1. Arguments and Conflicts
Siblings engaged in rivalry may frequently engage in verbal arguments, disagreements and conflicts. These conflicts can range from minor disagreements to more heated disputes over possessions, personal space or perceived slights.
2. Jealousy and Resentment
Sibling rivalry often involves feelings of jealousy and resentment. A sibling may feel envious of another sibling’s achievements, attention from parents or privileges leading to negative emotions and a sense of unfairness.
3. Sibling Comparison
Siblings engaged in rivalry may constantly compare themselves to each other. They may feel the need to measure up to their sibling’s achievements or abilities, which can create a competitive and hostile environment within the family. This can also lead to corroded self-esteem if one sibling is unable to match the superiority of the others.
4. Competition for Attention:
Siblings may compete for parental attention and affection. They may exhibit attention-seeking behaviors or vie for recognition and praise, sometimes resorting to negative behaviors if they feel neglected or overshadowed by their sibling. The same behaviours may manifest within extended family and peers.
5. Sabotage and Manipulation:
In extreme cases, sibling rivalry may involve acts of sabotage or manipulation. Siblings may intentionally undermine each other’s efforts, spread rumors or engage in manipulative tactics to gain an advantage, gain approval, recognition or attention.
6. Physical Aggression:
Sibling rivalry can escalate to physical aggression in some instances. Siblings may resort to hitting, pushing, or other physical acts of aggression as a means to assert dominance, retaliate or express pent up negative emotions.
7. Exclusion and Social Isolation:
Siblings engaged in rivalry may exclude or isolate each other from social activities or peer groups. They may intentionally withhold information or opportunities from one another, contributing to feelings of alienation and loneliness. This happens when one sibling wants to maintain the status quo of always being favoured or wanting to sabotage the sibling who gets all the attention, love, good grades, etc.
8. Constant Comparisons and Criticism
Sibling rivalry often involves constant comparisons and criticism amongst themselves. Siblings may frequently criticize and belittle each other’s choices, appearance or abilities. This further exacerbates feelings of rivalry and self-esteem issues in each other.
9. Displaying Infantile Behaviour
This is more common in younger children where they act like infants or toddlers. For example, a child may ask for a pacifier, swaddle or may want to breastfeed. In extreme cases, the regression might be too severe resulting to loss of previously formed skills e.g control of bowel and bladder function and appearance of distorted speech. Children often copy the actions of the younger child to attract the attention of parents. They stop eating, dressing or doing it ineptly, as if they need help from the mother.

How To Manage Sibling Rivalry
When it comes to dealing with sibling rivalry, the impeccable thing to keep in mind is to address the cause not the symptoms.
1. Open parent-child communication
Open communication refers to an environment where members of a family feel free to express their thoughts, opinions and ideas without any fear of repercussions. This condition brings about knowing each other on a deeper level, honesty and trust. As a parent, strive to model healthy and open communication in your family and encourage your children to embody the same.
Open and honest communication mitigates sibling rivalry by fostering understanding, cooperation and empathy.
2. Equal treatment of siblings
Equal treatment of siblings is key because it wades off unpleasant feelings of favouritism which give rise to rivalry in the siblings. Feelings such as exclusion, favouritism, unfairness and inferiority which worsen rivalry are obliterated when children feel you treat them equally.
3. Non-intervention in sibling conflicts
Non-intervention means holding space for your children to solve their conflicts by themselves under your observation and guidance. This works well when you model healthy open communication as well as doing your part to maintain harmonious relationships between your children. If nurtured well in children, this one of the best ways to avert sibling rivalry.
To equip your children to manage their conflict as they grow especially through teenagehood and into adulthood, consider inculcating the following useful life skills:
- How to negotiate
- Respect – especially towards younger and physically smaller siblings
- Assertive communication especially for introverted children
- Being considerate of how one’s actions and words impact others.
- Conflict resolution (explored further below)
4. Distraction
This technique works well for younger children. It is effective owing to the child’s short attention span. However, it is ineffective for older children and adolescents because they can think and act independently. In addition, they are not easily distracted from their intense feelings. During this developmental period, seek to equip them with skills to resolve conflicts by themselves without acting in a way that hurts them or another person. Offer your guidance until they master how to do it without your support.
5. Work on improving your conflict resolution skills
Your children will emulate how you handle conflict. By nature, children learn more by observation. How you manage conflict between you and your spouse, you and your children, you and any other person becomes the blueprint that your child will use. It is therefore imperative that you learn how to handle conflicts with poise and finesse, ultimately protecting the relationships and most importantly, your character.
Some methods of conflict resolution are detrimental and leave behind charred relationships and wounded people. Examples include withholding critical information, name-calling, blaming, verbal or physical abuse among others. Such methods, if adopted by children, exacerbate sibling rivalry and stunt emotional growth.
Helpful ways to model in your conflict management include:
- Allowing each one to fully express their feelings and thoughts about the situation
- Jointly identifying the conflict
- Taking accountability and each one owning the part they played
- Collaborating in finding solutions
- Agreeing on a solution
- Implementing the solution
A simple structure as outlined above is easy to model in children. It upholds respect, accountability, compromise and collaboration. These are vital skills required in order to maintain healthy relationships.
EXPLORE




2 thoughts on “Understanding And Managing Sibling Rivalry”
Awesome